A permanently cemented-in-place crown or bridge is categorized as a fixed dental restoration, offering a durable and long-lasting solution for damaged or missing teeth. This article delves into the intricacies of permanently cemented crowns and bridges, exploring their benefits, drawbacks, procedure, aftercare, cost, insurance coverage, and alternatives.
Permanently Cemented Crowns and Bridges: A Comprehensive Guide
A permanently cemented-in-place crown or bridge is a type of dental restoration that is fixed to the teeth with dental cement. This type of restoration is typically used to restore the function and appearance of teeth that have been damaged by decay, trauma, or other factors.
Definitions and Categorization
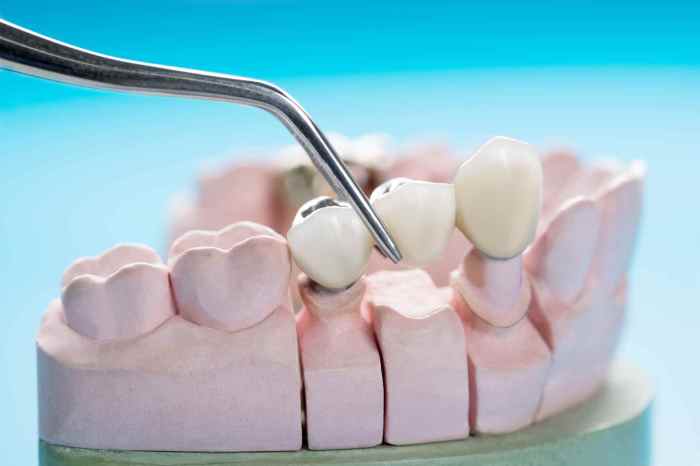
A crown is a cap that is placed over a tooth to restore its shape, size, and strength. A bridge is a fixed dental restoration that is used to replace one or more missing teeth. A permanently cemented-in-place crown or bridge is a type of restoration that is fixed to the teeth with dental cement and is not intended to be removed on a regular basis.
There are different types of permanently cemented-in-place crowns and bridges, including:
- All-ceramic crowns and bridges
- Metal-ceramic crowns and bridges
- Gold crowns and bridges
- Zirconia crowns and bridges
Benefits and Drawbacks: A Permanently Cemented-in-place Crown Or Bridge Is Categorized As A
Benefits, A permanently cemented-in-place crown or bridge is categorized as a
- Permanently cemented-in-place crowns and bridges are durable and can last for many years.
- They can restore the function and appearance of damaged or missing teeth.
- They can protect teeth from further damage.
Drawbacks
- Permanently cemented-in-place crowns and bridges are more expensive than other types of dental restorations.
- They require more preparation of the teeth than other types of restorations.
- They can be more difficult to clean than other types of restorations.
- During the first visit, the dentist will prepare the teeth for the restoration. This involves removing any decay or damaged tissue and shaping the teeth so that the crown or bridge will fit properly.
- The dentist will then take impressions of the teeth so that the crown or bridge can be fabricated.
- At the second visit, the dentist will place the crown or bridge on the teeth and cement it in place.
- Removable partial dentures
- Dental implants
- Maryland bridges
Procedure and Aftercare
The procedure for getting a permanently cemented-in-place crown or bridge typically involves multiple visits to the dentist.
After getting a permanently cemented-in-place crown or bridge, it is important to follow the dentist’s instructions for care. This includes brushing and flossing the teeth regularly and avoiding chewing on hard foods.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
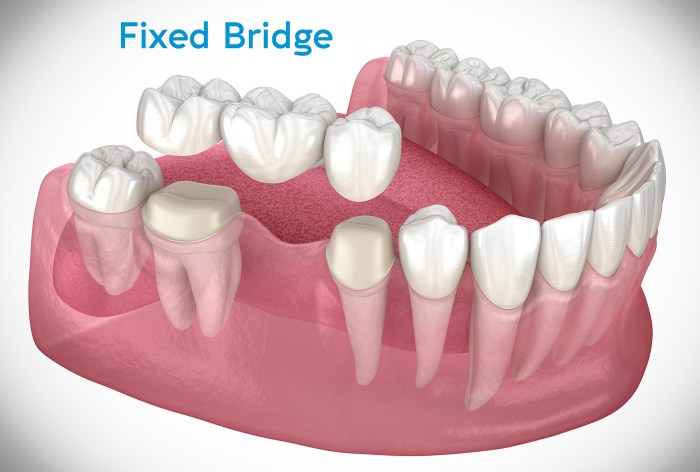
The cost of a permanently cemented-in-place crown or bridge varies depending on the type of restoration, the materials used, and the dentist’s fees.
Some dental insurance plans cover the cost of permanently cemented-in-place crowns and bridges. However, the coverage may vary depending on the plan.
To save money on the cost of a permanently cemented-in-place crown or bridge, it is important to shop around and compare prices from different dentists.
Alternatives to Permanent Cementation
There are a number of different types of dental restorations that can be used as alternatives to permanently cemented-in-place crowns and bridges.
The type of alternative restoration that is best for a particular patient will depend on the individual’s needs and preferences.
Detailed FAQs
What are the benefits of permanently cemented crowns and bridges?
Permanently cemented crowns and bridges offer several advantages, including enhanced durability, improved aesthetics, increased functionality, and protection of the underlying tooth structure.
Are there any drawbacks to permanently cemented crowns and bridges?
Potential drawbacks include the irreversible nature of the procedure, potential discomfort during the initial adjustment period, and the need for ongoing maintenance and care.
How long do permanently cemented crowns and bridges last?
With proper care and maintenance, permanently cemented crowns and bridges can last for many years, providing a long-term solution for dental restoration.