Discover the cells exhibition lab answer key and embark on an extraordinary journey into the fascinating world of cells, the fundamental units of life. This comprehensive guide will unravel the complexities of cell biology, providing you with a deep understanding of cell types, structures, processes, and functions.
Prepare to be captivated as we delve into the intricacies of cell division, metabolism, and homeostasis. Explore the techniques of cell culture, imaging, and analysis, unlocking the secrets of cellular behavior and function. Get ready to witness interactive displays and demonstrations that bring the world of cells to life, making learning an unforgettable experience.
Cells Exhibition Lab Overview
The Cells Exhibition Lab is an interactive and educational exhibit that explores the fascinating world of cells, the building blocks of all living organisms.
Established in 2015, the lab aims to provide visitors with a comprehensive understanding of cell biology, from their structure and function to their role in health and disease.
Target Audience and Educational Value
The Cells Exhibition Lab is designed for a wide range of audiences, including students, educators, and the general public. It serves as a valuable resource for:
- Students learning about cell biology as part of their science curriculum.
- Educators seeking to enhance their knowledge and teaching skills in cell biology.
- The general public interested in exploring the wonders of the human body and the latest advancements in cell research.
Lab Setup and Materials
To ensure a successful Cells Exhibition Lab, proper setup and organization are crucial. This involves gathering the necessary equipment and materials, organizing the lab space efficiently, and establishing clear safety guidelines for handling materials.
The following sections provide detailed information on the equipment, materials, setup, and safety protocols to facilitate a well-structured and safe lab environment.
Necessary Equipment and Materials
- Microscopes: Compound light microscopes are essential for viewing and studying cells.
- Slides and coverslips: These are used to prepare and mount cell samples for microscopic examination.
- Staining reagents: Dyes and stains are used to enhance the visibility and contrast of cellular components.
- Dissection tools: Scalpels, forceps, and scissors are used for dissecting and preparing cell samples.
- Safety goggles and gloves: These are essential personal protective equipment (PPE) for handling chemicals and biological materials.
- Centrifuge: This device is used to separate cells from other components in a sample.
- Incubator: An incubator is used to maintain a controlled environment for cell culture experiments.
- Cell culture media and reagents: These are essential for growing and maintaining cell cultures.
Lab Space Setup and Organization
The lab space should be organized to facilitate efficient workflow and minimize contamination. Designated areas should be established for specific tasks, such as sample preparation, microscopy, and waste disposal.
Microscopes should be placed on stable surfaces with adequate lighting. Workstations should be equipped with the necessary equipment and materials to avoid unnecessary movement and contamination.
Safety Guidelines and Protocols
Strict adherence to safety guidelines is essential to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of participants. The following protocols should be followed:
- Always wear appropriate PPE, including safety goggles and gloves, when handling chemicals or biological materials.
- Handle sharp objects with care and dispose of them properly in designated sharps containers.
- Follow proper disposal procedures for biological waste and chemical reagents.
- Report any accidents or spills immediately to the instructor or supervisor.
- Keep the lab space clean and organized to minimize contamination and accidents.
Cell Types and Structures
Cells, the fundamental units of life, exhibit remarkable diversity in their structures and functions. Understanding these variations is crucial for comprehending the complexity of biological systems.
Cell Types, Cells exhibition lab answer key
- Prokaryotic Cells:Lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles; typically found in bacteria.
- Eukaryotic Cells:Possess a nucleus and various membrane-bound organelles; include plant, animal, and fungal cells.
- Plant Cells:Have a cell wall made of cellulose, a large central vacuole, and chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
- Animal Cells:Lack a cell wall and chloroplasts; have centrioles involved in cell division.
Key Structures and Organelles
Nucleus:Controls cellular activities, housing DNA. Mitochondria:Generate energy (ATP) through cellular respiration. Ribosomes:Synthesize proteins based on DNA instructions. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER):Involved in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. Golgi Apparatus:Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion.
The cells exhibition lab answer key provides valuable insights into cell biology. Incidentally, if you’re interested in words with the root word “rupt,” here’s a helpful resource. Returning to the cells exhibition lab answer key, it’s essential for students to thoroughly review its contents to reinforce their understanding of cell structure and function.
Lysosomes:Contain digestive enzymes to break down waste and cellular debris. Vacuoles:Store substances, maintain water balance, and provide structural support in plant cells. Chloroplasts:Found in plant cells, contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Cell Processes and Function: Cells Exhibition Lab Answer Key
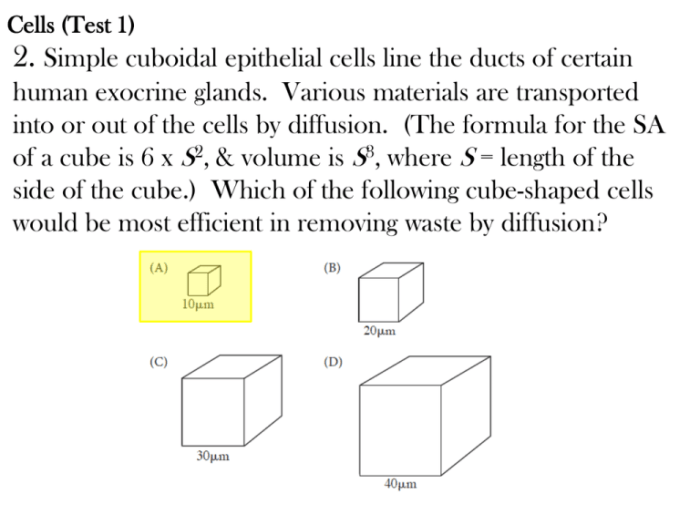
Cells are not static entities; they actively carry out various processes that are essential for their survival and the proper functioning of the organisms they constitute. These processes include cell division, metabolism, and maintaining homeostasis.
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. It is essential for growth, repair, and reproduction. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
- Mitosisis the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. It is used for growth and repair.
- Meiosisis the process by which a cell divides into four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It is used for sexual reproduction.
Cell Metabolism
Cell metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions that occur within a cell. These reactions are essential for the cell to obtain energy, synthesize new molecules, and remove waste products.
- Energy production: Cells obtain energy by breaking down glucose in a process called cellular respiration.
- Synthesis: Cells use energy to synthesize new molecules, such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
- Waste removal: Cells remove waste products, such as carbon dioxide and urea, through a process called excretion.
Maintaining Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment within an organism. Cells play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis by regulating various processes, such as:
- Temperature regulation: Cells can generate heat to maintain a constant body temperature.
- pH regulation: Cells can buffer acids and bases to maintain a constant pH level.
- Ion concentration regulation: Cells can regulate the concentration of ions, such as sodium and potassium, to maintain a constant osmotic balance.
Cell Culture Techniques
Cell culture techniques involve growing cells outside their natural environment, allowing scientists to study their behavior, function, and responses to various stimuli. These techniques are widely used in research and biotechnology applications.
Cell culture methods include:
- Primary culture:Directly obtained from living tissue, these cells retain their original characteristics but have a limited lifespan.
- Established cell lines:Derived from primary cultures, these cells can divide indefinitely and are used for long-term studies.
- Stem cell culture:Involves growing stem cells that can differentiate into various cell types.
Cell culture requires specific media and growth conditions tailored to the cell type. The media provides essential nutrients, growth factors, and pH balance. Growth conditions include temperature, humidity, and gas exchange.
Applications of Cell Culture
Cell culture techniques have numerous applications in research and biotechnology:
- Disease modeling:Studying cell behavior in diseases like cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and infectious diseases.
- Drug development:Testing drug efficacy and toxicity on cultured cells.
- Tissue engineering:Growing cells on scaffolds to create functional tissues for transplantation.
- Biotechnology:Producing proteins, vaccines, and other therapeutic products using cultured cells.
Cell Imaging and Analysis

Cell imaging and analysis are crucial techniques in cell biology, allowing scientists to visualize and study cells at various scales. Microscopy is a fundamental tool for cell imaging, enabling researchers to observe cells in their native state or after specific treatments.
Microscopy Techniques
Microscopy encompasses a range of techniques that provide different levels of magnification and resolution. Light microscopy, such as bright-field and phase-contrast microscopy, utilizes visible light to generate images. Electron microscopy, including transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), uses electron beams to achieve higher resolution and reveal ultrastructural details.
Stains and Dyes
To enhance the visibility of specific cell structures, stains and dyes are employed. These substances bind to particular molecules or organelles within the cell, making them easier to observe under the microscope. For example, hematoxylin stains nuclei blue, while eosin stains cytoplasm pink.
Image Analysis
Once cell images are captured, they can be analyzed using various software tools. These tools allow researchers to measure cell size, count organelles, and quantify protein expression levels. Advanced image analysis techniques, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, are also employed to automate image processing and extract meaningful data.
Interactive Displays and Demonstrations
To make the lab more engaging, consider incorporating interactive displays and demonstrations that allow visitors to experience cell biology firsthand.
Here are some ideas:
| Display Name | Description | Materials | Educational Objectives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Maze | Visitors navigate a maze using a model of a cell, learning about different cell structures and functions along the way. | Cardboard, markers, cell structure models | Understand cell structure and function |
| Cell Division Dance Party | Visitors perform a choreographed dance that simulates the process of cell division. | Music, instructions | Understand the stages of cell division |
| Microscope Scavenger Hunt | Visitors use microscopes to search for specific cell structures in prepared slides. | Microscopes, prepared slides | Develop microscopy skills, identify cell structures |
| Cell Culture Time-Lapse | Visitors observe a time-lapse video of cells growing and dividing in a culture dish. | Culture dish, microscope, camera | Understand cell growth and division |
Common Queries
What is the purpose of the cells exhibition lab?
The cells exhibition lab aims to provide an interactive and engaging learning experience, fostering a deeper understanding of cell biology and its significance in life sciences.
What types of cells are covered in the lab?
The lab explores a wide range of cell types, including prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as plant and animal cells.
What techniques are used in the cell culture component of the lab?
The lab utilizes various cell culture techniques, such as media preparation, cell passaging, and microscopy.